What is Cyclospora?
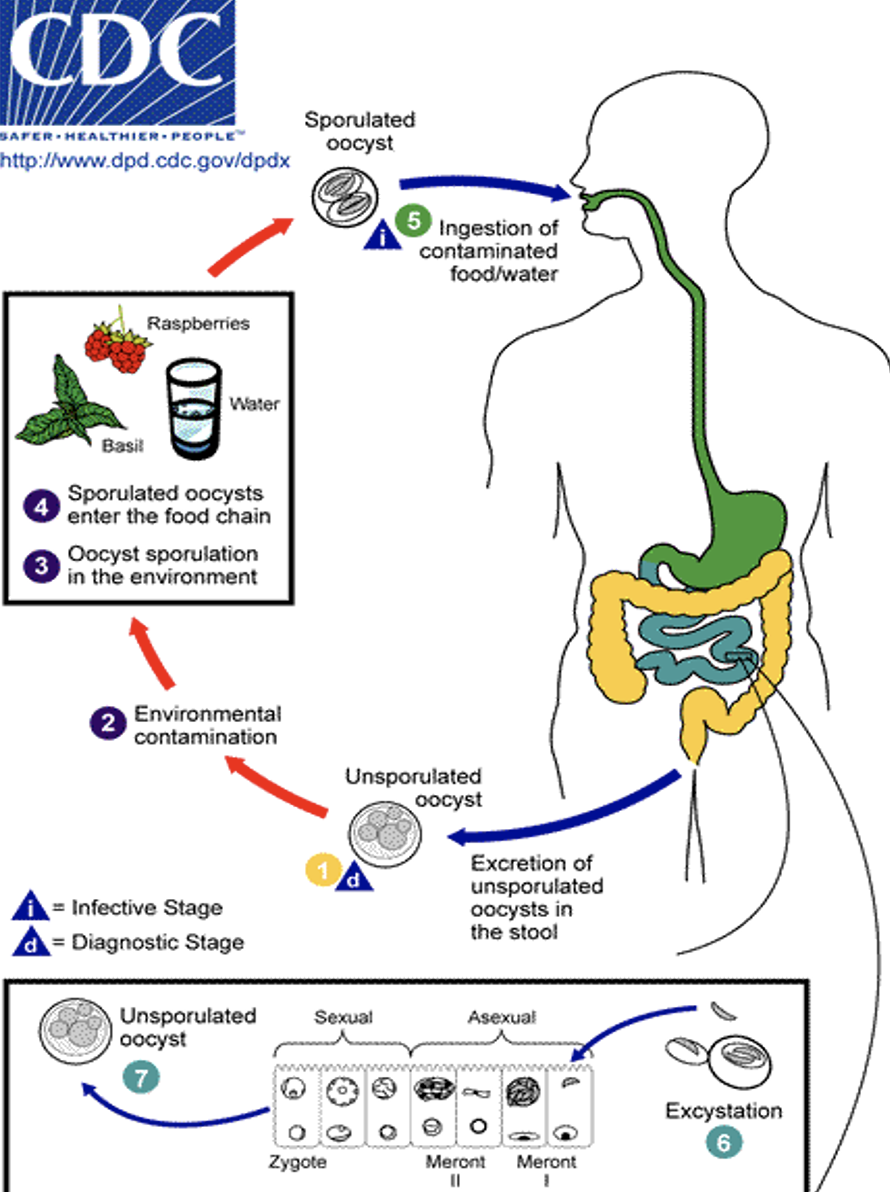
Cyclospora is a microscopic parasite that can cause food- or water-related gastrointestinal illness. Cyclospora cayetanensis is the only species of this organism found in humans.
How many illnesses occur in the United States?
In the United States, Cyclospora causes about 11,000 illnesses (cyclosporiasis) yearly.
Which Foods has Cyclospora been found in?
In North America, outbreaks of cyclosporiasis in humans have been reported mostly from contaminated fresh food products, such as soft fruits (raspberries, blackberries, and strawberries), leafy vegetables (lettuce and mixed salad), and herbs (basil and cilantro).
What are the impacts of cyclosporiasis?
Cyclospora infects the small intestine (bowel) and usually causes watery diarrhea, bloating, increased gas, stomach cramps, loss of appetite, nausea, low-grade fever, and fatigue. In some cases, vomiting, explosive diarrhea, muscle aches, and substantial weight loss can occur.
Since Cyclospora infections tend to respond to the appropriate treatment, complications are more likely to occur in individuals who are not treated or not treated promptly. These can include disorders of malabsorption, reactive arthritis, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), and, possibly, Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
A recent Cyclospora Outbreak:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), along with health departments in 14 states and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), investigated a national outbreak of Cyclospora in the summer of 2020.
As of September 23, 2020, a total of 701 lab-confirmed cases were found to be associated with this outbreak from 14 states (GA (1), IL (211), IA (206), KS (5), MA (1), MI (4), MN (86), MO (57), NE (55), ND (6), OH (7), PA (2), SD (13), WI (47). Exposures were reported in 13 states (IL, IA, KS, MA, MI, MN, MO, NE, ND, OH, PA, SD, WI). Cases reported illness from May 11, 2020 to July 24, 2020. Five percent were hospitalized, and no deaths were reported. Cases ranged from 11 to 92 years of age (median of 57). Fifty-one percent of cases were female.
In Canada, as of November 4, 2020, 370 confirmed cases of Cyclospora illness were reported in the following provinces and territories: British Columbia (1), Ontario (255), Quebec (105), New Brunswick (1), Newfoundland and Labrador (6), and Nunavut (2). Individuals became sick between mid-May and late August 2020. Ten individuals were hospitalized. No deaths were reported. Individuals who became ill are between 0 and 83 years of age. The illnesses are distributed equally among men (50%) and women (50%). Epidemiological and traceback evidence indicated that bagged salad mix containing iceberg lettuce, carrots and red cabbage by Fresh Express was the likely source of this outbreak. Further traceback efforts by the FDA led to the investigation of a farm in southern Florida. The FDA detected Cyclospora in a regional water management canal (C-23), located west of Port St. Lucie, Florida. However, the FDA has been unable to determine if this Cyclospora was a genetic match to cases associated with the outbreak. Nevertheless, the presence of Cyclospora in a canal that had previously supplied irrigation water in the region, and specifically to a farm identified in the traceback, was suspicious and requires the need for further investigation and response from the FDA and it’s investigating partners. Fresh Express recalled salad products produced at its Streamwood, Illinois facility on June 27, 2020. The Fresh Express recall included only those salads products containing the ingredients iceberg lettuce, red cabbage and/or carrots AND displaying the Product Code Z178, or a lower number. Recalled products were distributed to select retail stores – including ALDI, Giant Eagle, Hy-Vee, Jewel-Osco, ShopRite, and Walmart – between June 6 and June 26 in various states. The recalled retail store brands were ALDI Little Salad Bar, Giant Eagle, Hy-Vee, Jewel-Osco Signature Farms, ShopRite Wholesome Pantry, and Walmart Marketside. The “Best by” date on the recalled products ran through July 14, 2020. As of September 23, 2020, the outbreak was considered over.